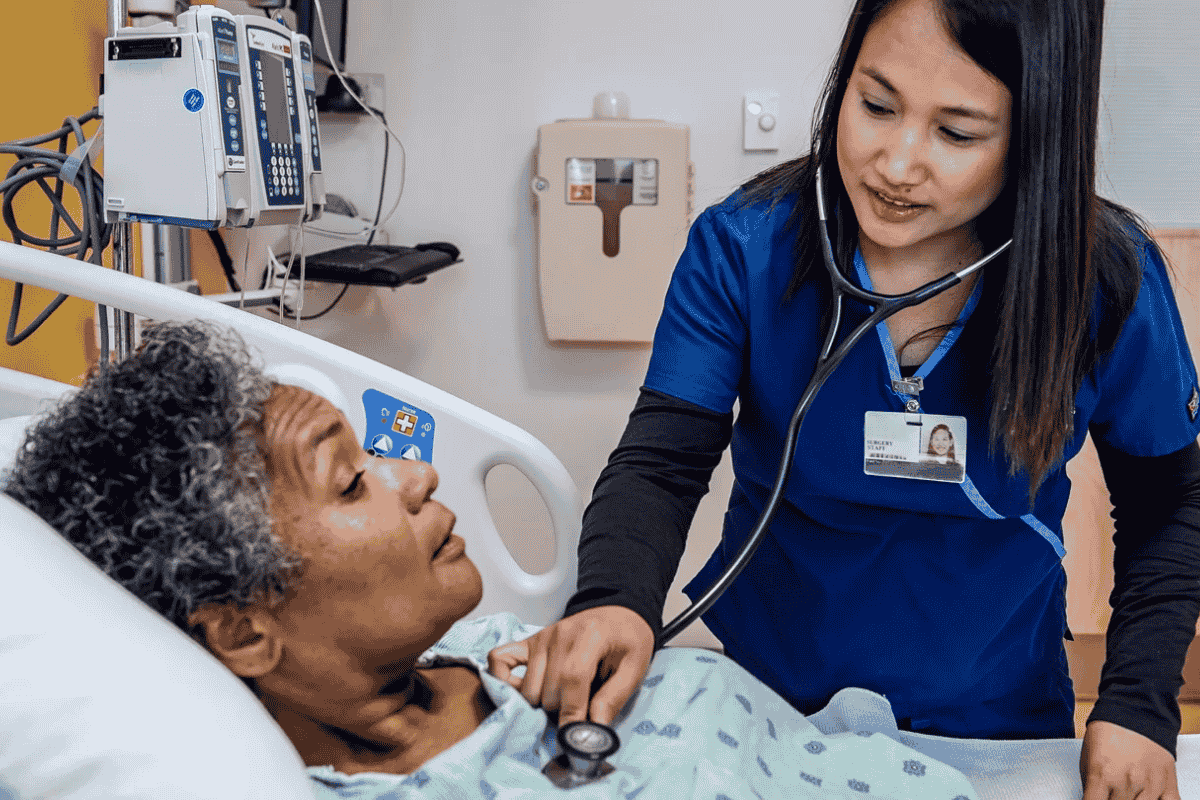
In today’s fast-changing world, nursing is more than just a profession—it’s the heart of the healthcare system. From the moment a patient enters the system to the time they recover, nurses are there, providing care, support, and expert guidance.
They are the ones who connect patients, families, doctors, and other healthcare professionals to ensure smooth, effective treatment. But nursing today is not just about compassion—it’s a powerful mix of science, skill, and deep human understanding.
The Evolving Role of Nurses in Modern Healthcare
Nursing in the 21st century is a dynamic, ever-evolving profession. Nurses don’t just follow doctor’s orders—they often lead the way in diagnosing conditions, offering emotional support, and educating the public about health issues.
Whether it’s managing chronic illnesses, assisting in surgeries, or giving preventive care, nurses play a central role in every step of a patient’s healthcare journey.
They are found in hospitals, clinics, schools, correctional facilities, camps, and even homes—anywhere there is a need for care. Their work isn’t just about treating illness—it’s about promoting overall wellness.
The Science and Art of Nursing
Nursing is often described as both an art and a science. The art lies in understanding people, having compassion, and providing comfort. The science comes from years of education, training, and clinical knowledge.
Every nurse brings unique skills, passions, and specialisations, but they all share a common goal: giving the best care to every patient.
They do more than read test results—they observe, listen, and understand both the physical and emotional needs of the patient. This combination of critical thinking and deep empathy makes nursing a truly holistic profession.
What Do Nurses Actually Do?
Nurses have a wide range of responsibilities depending on their role, setting, and experience. Some nurses handle emergency situations, while others focus on long-term care or prevention. But there are a few common things that most nurses do:
- Monitor and record patient health
- Assist in diagnosis and treatment
- Educate patients and families about conditions and care plans
- Give medications and treatments
- Support patients emotionally and physically
No matter the task, nurses always keep the patient’s wellbeing as the top priority.
Types of Nurses and Their Roles
There are different types of nurses, each with specific training and responsibilities. Here’s a look at the major types:
Registered Nurses (RNs)
RNs form the backbone of the nursing workforce. They work in every healthcare setting and handle a wide variety of duties.
Main Responsibilities:
- Do physical exams and take patient histories
- Educate patients about health and treatment
- Give medications and manage care
- Work closely with doctors and other healthcare professionals
Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs)
APRNs have advanced education (usually a Master’s degree) and can perform many duties traditionally done by doctors.
Roles include:
- Nurse Practitioners (NPs): Diagnose and treat illnesses, prescribe medicine
- Certified Nurse-Midwives (CNMs): Provide care during pregnancy and childbirth
- Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs): Handle complex health issues, both mental and physical
- Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs): Administer anesthesia in surgeries and procedures
Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs)/Licensed Vocational Nurses (LVNs)
LPNs and LVNs provide basic care under the supervision of RNs or doctors.
Main Responsibilities:
- Take vital signs and monitor patient condition
- Help with bathing, dressing, and feeding
- Change bandages and help with wound care
- Give medications (in some settings)
Understanding the Nursing Process
All nurses, no matter their role, follow the same five-step nursing process to ensure top-quality care:
- Assessment – Gather detailed information about the patient’s condition, lifestyle, and needs.
- Diagnosis – Identify health problems based on symptoms and observations.
- Planning – Set clear goals for recovery and create a care plan.
- Implementation – Carry out the plan with care and attention.
- Evaluation – Review the results and make changes if needed for better outcomes.
This structured approach helps nurses give personalised and effective care to every patient.
Nurses: The Pillars of Public Health
With over 4 million registered nurses in the United States, it’s clear how essential they are. Nurses are present in every corner of the country, helping people live healthier lives from birth to end-of-life care.
However, reports have shown that there could be a shortage of nurses in many parts of the country, especially in the South and West, by 2030.
Nurses today are not just caregivers—they are leaders, educators, advocates, and innovators. They help create healthcare policies, improve quality standards, and manage entire care systems.
Nursing in the 21st century is one of the most vital and respected professions in the world. Nurses are the heart of healthcare—always present, always caring, and always learning.
As the healthcare system grows more complex, the role of nurses becomes even more critical. With their unique combination of compassion, expertise, and dedication, nurses ensure that patients get the best care possible—anytime, anywhere.